Carbon Monoxide Transport from California Wildfires, July 30-August 7, 2018
Click on above for larger animation
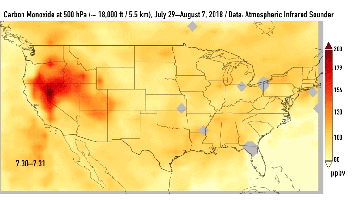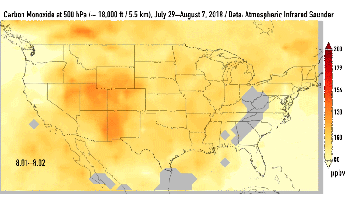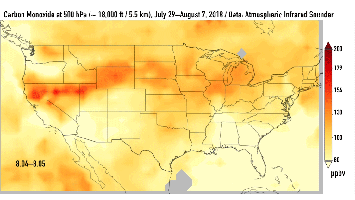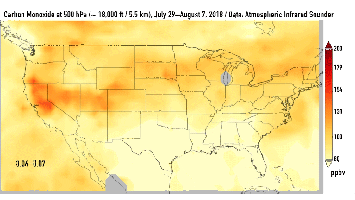
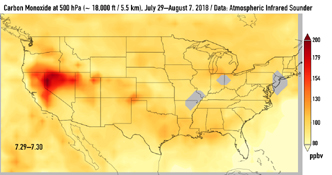
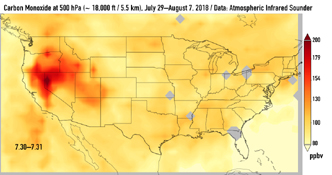
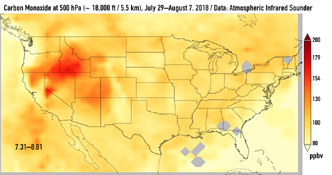
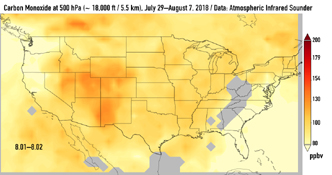
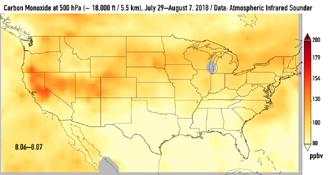
This series of images shows carbon monoxide (in orange/red) from California's massive wildfires drifting east across the U.S. between July 30 and August 7, 2018. It was produced using data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite.
AIRS measures concentrations of carbon monoxide that have been lofted high into the atmosphere. These images show the carbon monoxide at a 500 hPa pressure level, or an altitude of approximately 18,000 feet (5,500 meters). As the time series progresses, we see that this carbon monoxide is drifting east with one branch moving toward Texas and the other forking to the northeast. The high end of the scale is set to 200 parts per billion by volume (ppbv); however, local values can be significantly higher.
Carbon monoxide is a pollutant that can persist in the atmosphere for about one month and can be transported large distances. It plays a role in both air pollution and climate change.
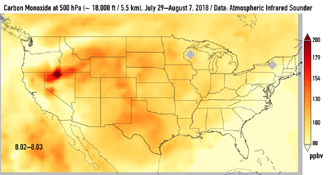
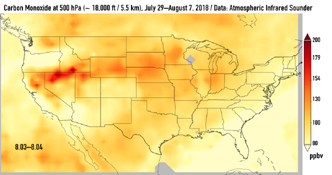
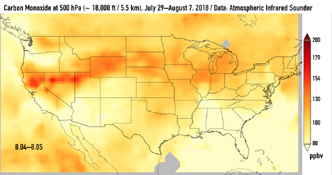
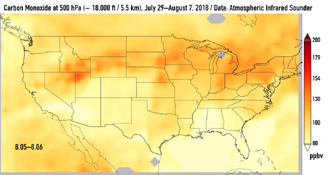
Click on an image above for larger view
About AIRS
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, in conjunction with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit, AMSU, senses emitted infrared and microwave radiation from Earth to provide a three-dimensional look at Earth's weather and climate. Working in tandem, the two instruments make simultaneous observations all the way down to Earth's surface, even in the presence of heavy clouds. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, three-dimensional map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations, and many other atmospheric phenomena. Launched into Earth orbit in 2002, the AIRS and AMSU instruments fly onboard NASA's Aqua spacecraft and are managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at https://airs.jpl.nasa.gov.
