Typhoon Ioke in the Western Pacific
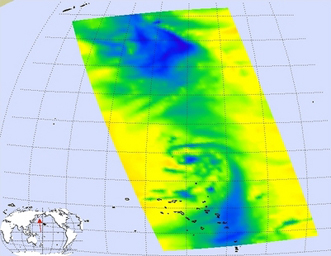 | 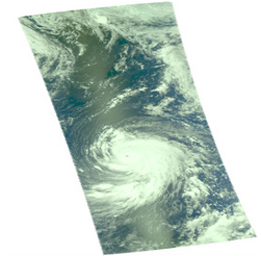 |
| Microwave Image | Visible Light Image |
These infrared, microwave, and visible images were created with data retrieved by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite.
Infrared Image
Because infrared radiation does not penetrate through clouds, AIRS infrared images show either the temperature of the cloud tops or the surface of the Earth in cloud-free regions. The lowest temperatures (in purple) are associated with high, cold cloud tops that make up the top of the storm. In cloud-free areas the AIRS instrument will receive the infrared radiation from the surface of the Earth, resulting in the warmest temperatures (orange/red).
Microwave Image
In the AIRS microwave imagery, deep blue areas in storms show where the most precipitation occurs, or where ice crystals are present in the convective cloud tops. Outside of these storm regions, deep blue areas may also occur over the sea surface due to its low radiation emissivity. On the other hand, land appears much warmer due to its high radiation emissivity.
In the AIRS microwave imagery, deep blue areas in storms show where the most precipitation occurs, or where ice crystals are present in the convective cloud tops. Outside of these storm regions, deep blue areas may also occur over the sea surface due to its low radiation emissivity. On the other hand, land appears much warmer due to its high radiation emissivity.
Microwave radiation from Earth's surface and lower atmosphere penetrates most clouds to a greater or lesser extent depending upon their water vapor, liquid water and ice content. Precipitation, and ice crystals found at the cloud tops where strong convection is taking place, act as barriers to microwave radiation. Because of this barrier effect, the AIRS microwave sensor detects only the radiation arising at or above their location in the atmospheric column. Where these barriers are not present, the microwave sensor detects radiation arising throughout the air column and down to the surface. Liquid surfaces (oceans, lakes and rivers) have "low emissivity" (the signal isn't as strong) and their radiation brightness temperature is therefore low. Thus the ocean also appears "low temperature" in the AIRS microwave images and is assigned the color blue. Therefore deep blue areas in storms show where the most precipitation occurs, or where ice crystals are present in the convective cloud tops. Outside of these storm regions, deep blue areas may also occur over the sea surface due to its low radiation emissivity. Land appears much warmer due to its high radiation emissivity.
Vis/NIR Image
The AIRS instrument suite contains a sensor that captures radiation in four bands of the visible/near-infrared portion of the electromagetic spectrum. Data from three of these bands are combined to create "visible" images similar to a snapshot taken with your camera.
About AIRS
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, in conjunction with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit, AMSU, senses emitted infrared and microwave radiation from Earth to provide a three-dimensional look at Earth's weather and climate. Working in tandem, the two instruments make simultaneous observations all the way down to Earth's surface, even in the presence of heavy clouds. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, three-dimensional map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations, and many other atmospheric phenomena. Launched into Earth orbit in 2002, the AIRS and AMSU instruments fly onboard NASA's Aqua spacecraft and are managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at http://airs.jpl.nasa.gov.
