AIRS First Light Data: Northern Europe, July 20, 2002
 |  |  |
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
These images, taken over northern Europe on July 20, 2002, depict a few of the different views of Earth and its atmosphere that are produced by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder experiment system operating on NASA's Aqua spacecraft.
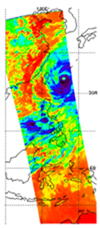
The image in Figure 1 is from an infrared channel from the AIRS instrument that measures the surface temperature in clear areas and cloud top temperatures in cloudy areas. The image reveals very warm conditions in France and a storm off the east coast of the United Kingdom.
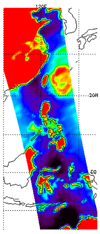
The image in Figure 2 represents a microwave channel from the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit instrument that sees through most clouds and observes surface conditions everywhere.
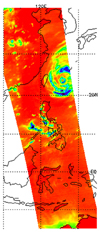
The image in Figure 3 is a microwave channel from the Humidity Sounder for Brazil instrument that is very sensitive to humidity and does not see the surface at all, but instead reveals the structure of moisture streams in the troposphere.
The infrared and microwave data from the AIRS experiment are integrated to retrieve a single set of temperature, moisture, and cloud values. These three channels represent only a small portion of the 2,400-channel multispectral experiment, whose primary objectives are to improve the accuracy of weather forecasts and to study climate change.
The AIRS experiment system also takes pictures of the Earth at four visible and near-infrared wavelengths that can be combined into a color picture. This image shows a swirling low-pressure system over England, clear skies over much of France, and frontal systems in the North Atlantic. Because AIRS is sensitive to different wavelengths than your eye, the colors shown are different from what you would see. For example, plants appear very red to AIRS. There are also subtle color differences in the clouds that relate to their altitude and thickness (compare the white clouds over England with the slightly grey-green ones near Iceland). These images are used in conjunction with other AIRS, AMSU-A, and HSB measurements to get a full 3-D view of the atmosphere.
About AIRS
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, in conjunction with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit, AMSU, senses emitted infrared and microwave radiation from Earth to provide a three-dimensional look at Earth's weather and climate. Working in tandem, the two instruments make simultaneous observations all the way down to Earth's surface, even in the presence of heavy clouds. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, three-dimensional map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations, and many other atmospheric phenomena. The Humidity Sounder for Brazil, HSB, is a 4-channel microwave sounder provided by Brazil that obtained humidity profiles throughout the atmosphere even under conditions of heavy cloudiness and haze. The HSB provided high quality data until February 2003. Launched into Earth orbit in 2002, the AIRS, AMSU, and HSB instruments fly onboard NASA's Aqua spacecraft and are managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at http://airs.jpl.nasa.gov.
