EMIT Spots Methane Hotspots
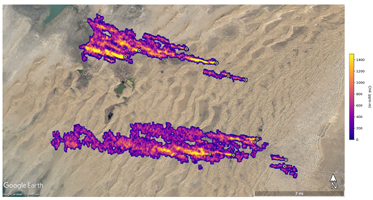
Figure A
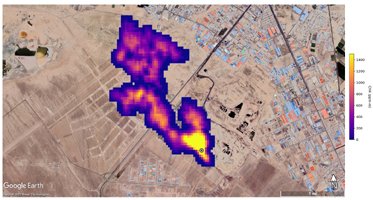
Figure B
Click on images for larger versions
A plume of methane – a potent greenhouse gas about 80 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide – is detected flowing from an area southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico, in an image that uses data from NASA's Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) mission. The 2-mile (3.3-kilometer) long plume originates in an area known as the Permian Basin, which spans parts of southeastern New Mexico and western Texas and is one of the largest oilfields in the world.
EMIT uses an imaging spectrometer to detect the unique pattern of reflected and absorbed light – called a spectral fingerprint – from various materials on Earth's surface and in its atmosphere. Perched on the International Space Station, EMIT was originally intended to map the prevalence of minerals in Earth's arid regions, such as the deserts of Africa and Australia. Scientists verified that EMIT could also detect methane and carbon dioxide when they were checking the accuracy of the image spectrometer's mineral data.
Figure A shows 12 plumes from oil and gas infrastructure east of Hazar, Turkmenistan, a port city on the Caspian Sea. Some of the plumes, which are blowing westward, stretch for more than 20 miles (32 kilometers).
Figure B shows a methane plume from a landfill south of Tehran, Iran, that is at least 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) long. Methane is a byproduct of the decomposition of organic material, and substantial emissions are often detected around landfills.
The data for these images was collected by EMIT in August 2022.
Scientists estimate flow rates of 20.2 tons (18.3 metric tons) per hour at the Permian site, 55.6 tons (50.4 metric tons) per hour in total for the Turkmenistan sources, and 9.4 tons (8.5 metric tons) per hour at the Iran site. While quite large, these emission rates are broadly consistent with previous studies of locations like the Permian Basin, as well as emission source types like landfills. The Turkmenistan example has a similar magnitude to the 2015 Aliso Canyon Blowout.
EMIT was selected from the Earth Venture Instrument-4 solicitation under the Earth Science Division of NASA Science Mission Directorate and was developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California. It launched aboard a SpaceX Dragon resupply spacecraft from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 14, 2022. The instrument's data will be delivered to the NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC) for use by other researchers and the public.
