Circumstellar Disk Around Fomalhaut


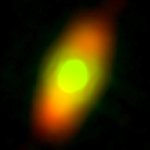
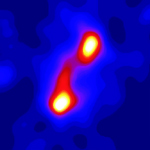
The NASA Spitzer Space Telescope has obtained the first infrared images of the dust disc surrounding Fomalhaut, the 18th brightest star in the sky. Planets are believed to form from such a flattened disc-like cloud of gas and dust orbiting a star very early in its life. The Spitzer telescope was designed in part to study these circumstellar discs, where the dust particles are so cold that they radiate primarily at infrared wavelengths. Located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus, the parent star and its putative planetary system is found at a distance of 25 light-years.
Twenty years ago, the Infrared Astronomical Satellite, the first orbiting infrared telescope, detected much more infrared radiation coming from Fomalhaut than was expected for a normal star of this type. The dust is presumed to be debris left over from the formation of a planetary system. However, the satellite did not have adequate spatial resolution to image the dust directly. Subsequent measurements with sub-millimeter radio telescopes suggested that Fomalhaut is surrounded by a huge dust ring 370 astronomical units (an astronomical unit is the average distance between the Sun and Earth), or 34 billion miles (56 billion kilometers) in diameter. This corresponds to a size of nearly five times larger than our own solar system. Moreover, the sub-millimeter observations (far right image) revealed that the ring was inclined 20 degrees from an edge-on view.
The new images obtained with the multiband imaging photometer instrument onboard Spitzer confirm this general picture, while revealing important new details of Fomalhaut's circumstellar dust. The 70-micron image (lower left) clearly shows an asymmetry in the dust distribution, with the southern lobe one-third brighter than the northern. Such an unbalanced structure could be produced by a collision between moderate-sized asteroids in the recent past (releasing a localized cloud of dust) or by the steering effects of ring particles by the gravitational influence of an unseen planet.
At 24 microns (upper left), the Spitzer image shows that the center of the ring is not empty. [Note that an image of a reference star was subtracted from the Fomalhaut image to reveal the faint disc emission.] Instead, the 'doughnut hole' is filled with warmer dust that extends inward to within at least 10 astronomical units of the parent star. This warm inner disc of dust occupies the region that is most likely to be occupied by planets and may be analogous to our solar system's 'zodiacal cloud' -- but with considerably more dust. One possible explanation for this warmer dust is that comets are being nudged out of the circumstellar ring by the gravitational influence of massive planets. These comets then loop in toward the central star, releasing dust particles just as comets do in our own solar system.
